POLYGON Pe-xb pipe, using one step method (MONSOIL) technology, adding silane modified raw materials, through high temperature steam fully cross-linked to form a stable three-dimensional network structure, so that crosslinked polyethylene has excellent physical and chemical properties, high temperature resistance, shape memory performance. Good flexibility for construction
Product Introduction
Environmental protection, non-toxic, tasteless, Corrosion Resistance
Temperature and pressure resistance it can be used in an environmental of minus 40 degrees, and can also be used in a high temperature environment of 110 degrees, Non-Scaling
Aging Resistance: It has good creep resistance and aging resistance.
Advanced Equipment, such as NOKIA-MAILLEFER Patent, One Step Monosil PE-X producing technology Stam-pressure cross-linking technology is used to reduce the longitudinal shrinkage.
Description
Name | PE-XB Pipe |
Material | Polyethylene |
Diameter | 16mm-63mm |
Series | S5/S4/S3.2/S2.5 |
Brand Name | POLYGON |
Certification | CE |
Welding Way | Fitting Connection |
Packing | Package |
Pressure | High Pressure |
Temperature | 0℃-95 |
Service Life | 50 years |
Delivery Time | 30 days after deposit |
Specification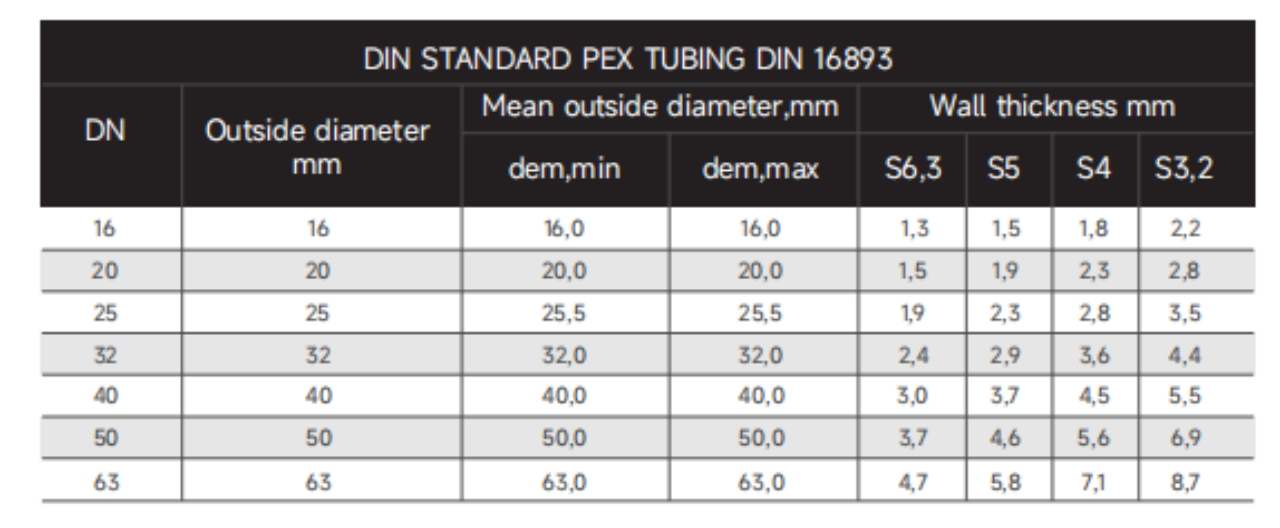
Application Field
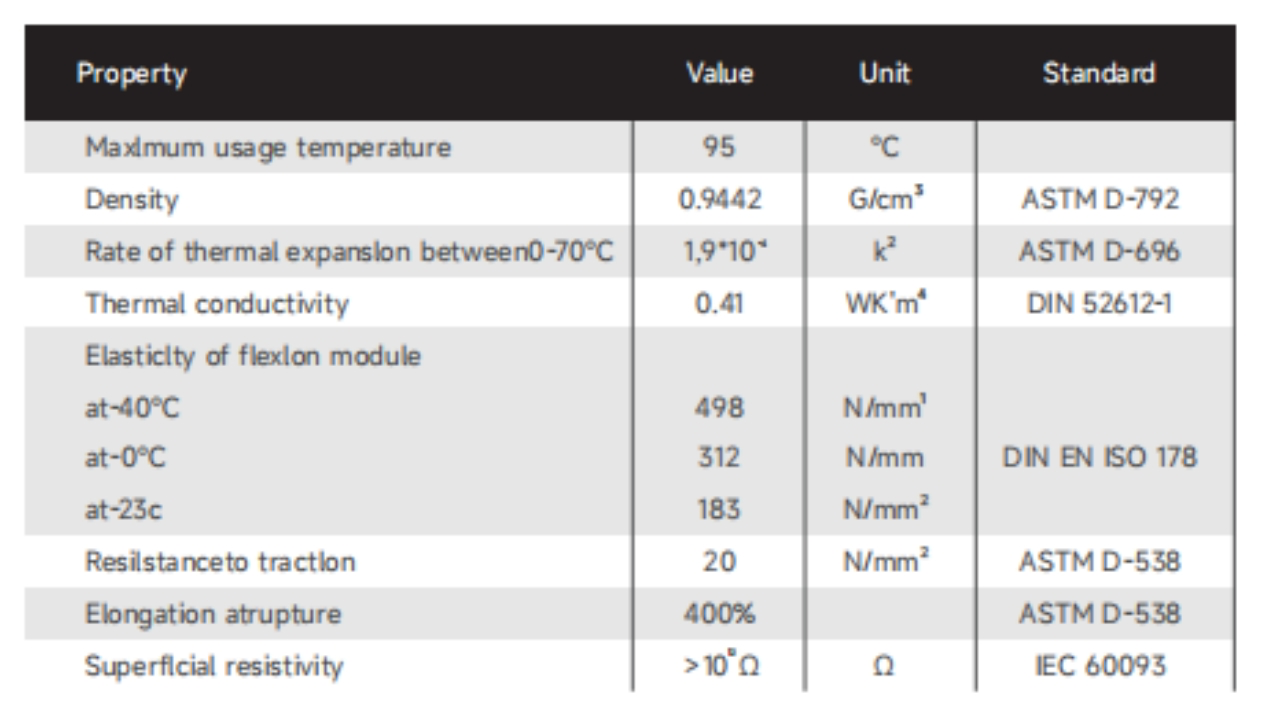
Technical Parameters
Q&A
What is Low-Temperature Hot-Water Radiant Floor Heating?
Low-temperature hot-water radiant floor heating is a type of heating system that uses hot water with a temperature no higher than 60°C as the heat medium. The water circulates through heating pipes embedded in the floor's filling layer, warming the entire floor. Heat is then transferred to the room primarily through radiation and partially through convection.
How to Explain That Floor Heating is Energy-Efficient and Environmentally Friendly?
Low-temperature floor radiant heating uses the entire indoor floor as a heat-emitting surface. The indoor air temperature can be 2–3°C lower than that of other heating methods, which alone can save about 10% of energy. Additionally, it can utilize geothermal energy and industrial waste heat as heat sources for floor radiant heating. The low-temperature transmission of the heat medium also reduces heat loss during the process.
Why is Floor Radiant Heating Known for Its Good Thermal Stability and Long Lifespan, and How Many Times Longer Than Radiators?
Due to the large heat storage capacity of the floor layer and the concrete layer, floor radiant heating has good thermal stability. Under intermittent heating conditions, the indoor temperature changes slowly. Polyethylene of Raised Temperature (PE-RT) pipes can be used continuously for over 50 years, which is six times the lifespan of ordinary radiators.
What is the Optimal Length of Each Loop in a Floor Heating System?
The length of each loop of the heating pipe should not exceed 120 meters. It is also required that the lengths of the heating pipes in each loop be as close to equal as possible. This is to ensure hydraulic balance.
How to Transport and Store Pipes and Fittings?
Pipes, fittings, and insulation boards should be handled with care during transportation, loading, and unloading. They must not be subjected to severe impacts or collisions with sharp objects. Throwing, dropping, rolling, or dragging should be avoided, and contact with oil should be prevented.
Pipes, fittings, and insulation boards should be stored in a well-ventilated warehouse with a temperature not exceeding 40°C. They should be kept away from fire and sunlight, with a minimum distance of 1 meter from heat sources. Outdoor storage should be avoided. The storage area should be clean and level to prevent dirt and debris from entering the pipes.
What is the Spacing for Laying Heating Pipes?
The spacing for laying heating pipes should ideally be between 100–300 mm, with a maximum spacing not exceeding 300 mm.

